Service on the Linux operating system known as daemons. This service was developed to allow a process running in the background without the need for direct interaction with the user. Most daemons are run by the system when the system is active (startup). Examples of Linux applications that fall into the category of this service is the Apache HTTP Server, Nginx HTTP Server, MySQL Database Server, and Open SSH Server.
Service is an application that is different from the application user. Its existence is capable of supporting a system that can run multiple processes at once (multitasking). Each service application that is run at startup on Linux /etc/rc*.d/ placed in the directory, where * is used to refer to a runlevel that have been determined during the process of init system. Scripts to change the status of a service is generally placed in the directory /etc/init.d/.
Changing the status of a service may be activation and deactivation of the service. The command is given following the conversion of its status, which can only be run by the root user.
/etc/init.d/skrip-daemon command
Commands herein may contain:
– Start: start the service
– Stop: stop the service
– Restart: stop and run back service
– Reload: read back the data and application services
– Status: display the status of the service
Examples of the above command, given in the following figure.
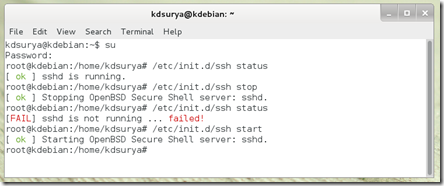
Figure 40. Example of command in Linux management services
The above command will cause ssh service is enabled by the system. Another way to operate the service is dengen using the following command.
service-daemon script command
Linux Startup Service
The command has just presented above for the service will not make these services run at computer startup. The following command can be used for this purpose.
Activation of the service startup: insserv script-daemon
Deactivation of the service startup: insserv -r script-daemon
If the SSH service has been installed then through the above command will disable the system startup for the SSH service. This can be proven by restarting the computer then reads the status of the SSH service.
Analysis can be done by looking at the status of the service. Besides through status, analysis can also be done through the reading of the records of activities (log) of the service.
Each service in Linux has a log file in text format that can be accessed or opened with a text editor application, such as the nano, more, paint, gedit, kwrite, and the like. In general, almost all the log files are stored by the Linux system in the directory / var / log /. More on log reading techniques can be seen in the material Troubleshooting Network Operating System.