(1) Moisture Wood
Wood contains water, the amount of water content varies greatly can achieve scrolled to 200% in fresh condition. Wood moisture content obtained from the ratio of the amount of water (by weight) than the weight of the air dry wood kiln dry wood, expressed in per cent (%) can be expressed by the formula:
Moisture MC
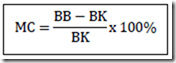
BB = Wet weight
BK = weight of dry kiln

Fig. Hydrometer
Besides by weighing, moisture content of wood can be measured using a measuring instrument moisture content of wood (Hydrometer, MC meter). Stages of evaporation in the wood can be described as follows:
(a) Wood Wet, every pore and cell wall cavity is filled with a water content of the wood. The water content can reach 200%.
(b) After logging Wood, after wood cut, hydrogen can not enter again. Wood cell walls remain filled with water, while the water in the cell cavities partially reduced. The amount of water content is still around 35% – 70%.
(c) Saturated Point fiber, cavity-free water in the pores of the wood has been out everything. The water content in the cell walls remain. Akadar water ranging between 25% – 30%.
(d) Dry Air / Moisture Balance Point, at this time, the wood adjust to the surrounding air, so that the water content in the cell walls begin evaporated keluar.Bentuk dimensional lumber began to change, wood moisture content between 12% – 20%
(e) Dry furnace, the pore cavities and cell walls do not contain water anymore. Heavy wood can not drop further. Wood moisture content 0%.
(2) Depreciation Wood
Shrinkage or shrinkage flower timber has a particular direction because of differences in the structure of the wood pores or trakeida on coniferous wood. In general there are 3 toward the development / major shrinkage in the wood, that is:
(a) Depreciation Tangential direction, shrinkage in the direction of the circle, the extent of decline ranging from 4.3% – 14%.
(b) Depreciation Radial direction, shrinkage direction of the timber or jar-finger circle cut perpendicular years, the extent of decline ranging from 2.1% – 8.5%.
(c) Depreciation direction Axial, shrinkage direction of the length of the wood, the magnitude of shrinkage ranging between 0.1% – 0.3%.