Judging from its function, the resistors can be divided into:
1. Fixed Resistors (Fixed Resistors)
Namely resistor whose value can not be changed, so always fixed (constant) .Resistor is usually made of Nikelin or karbon.Berfungsi as a voltage divider, regulate or limit the current in a circuit as well as enlarging and reducing stress.
2. Resistor Variable (variable resistor)
Namely resistor whose value can change with a shift or rotate the toggle on the tool, so that the value of the resistor can be set according to need. Serves as a volume control (adjust the size of the current), tone control on the sound system, regulating the level of tone (bass / treble) as well as serve as a voltage divider current and voltage.
3. Resistors NTC and PTC.
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient), a resistor whose value will become smaller when exposed to heat. While PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient), a resistor whose value will increase if the temperature becomes cold.
4. Resistor LDR
LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) are the type of resistor that changes its resistance due to the effect of exposure to light dark cahaya.Bila prisoner greater value, whereas when exposed to bright light value becomes smaller.
In practice, the designers sometimes require resistors with a certain value. However, the resistor values are not in store sellers, even the plant itself does not produce it. Solution to obtain a value that is unique resistor can be done by assembling a few resistors to obtain the required resistance value. There are two ways to weave resistor, namely:
1. How To Series
2. How to Parallel
The series resistor in series will result in greater total resistance value. Below is an example of resistors connected in series.
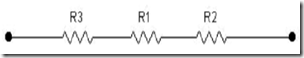
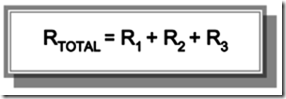
In the serial resistor circuits apply the formula:
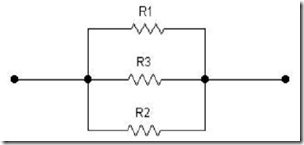
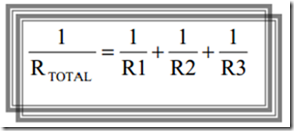
While the series resistor in parallel will result in replacement for the smaller resistance value. Below is an example of the resistors that are arranged in parallel.