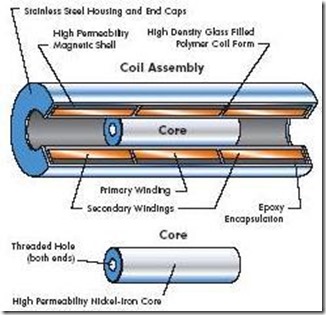
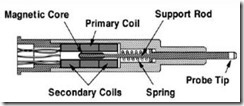
As the name implies linear means linear straight motion, this sensor reads the movement of a straight line, linearly. LVDT consists of:
- · The moving iron core
- · Primary coil
- · A pair of secondary coils
A. Primary Coil
Connected with AC voltage as reference voltage
B. Secondary Coil
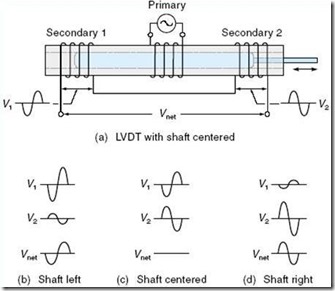
Numbered 2 pieces, located on the left and right side of the primary coil are connected in series with each other. The core is in the middle then:
Flux S1 = S2
Induced voltage E1 = E2
Enetto = 0
The core moves towards S1 then:
Flux S1> S2
induced voltage E1> E2, Enetto = E1 – E2
The core moves toward S2 then:
Flux S1 <S2
Induced voltage E1 <E2
Linear relationship when core is still around the equilibrium position Scheme and lvdt image
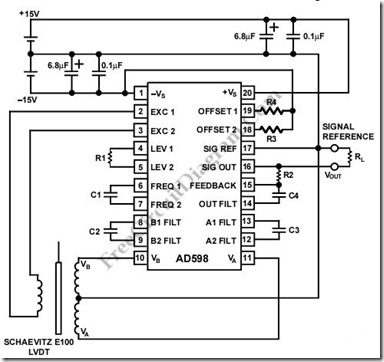
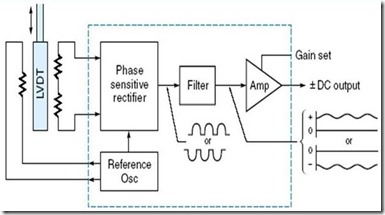
LVDT application of IC interface
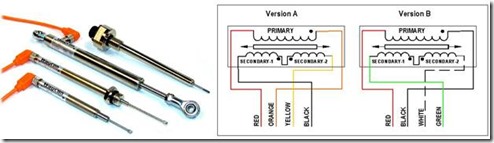
Examples of LVDT Sensor Implementation
Sensors (displacement, distance, and other mechanical sensors)
- · Fluid levels
- · Sensors (displacement, distance, and other mechanical sensors)
- · Automotive Suspension
- · ATM machine
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- · No friction between iron core and transformer
- · Unlimited resolution
- · Reliable and durable
- · Can be applied to various environments
- · Absolute output (absolute)
deficiency
- · Price is relatively expensive