The transformer (transformer) is an electric appliance / electronics which serves to move the energy (power) power from input to output or from the primary side to the secondary side. The transfer of power from the primary to the secondary is accompanied by a voltage change either up or down. There are two types of step-up transformer that is transformer voltage (step-up transformers) and lowering the voltage transformer (step-down transformers). If the primary voltage is smaller than the secondary voltage, the so-called step-up transformer. But if the primary voltage is greater than the secondary voltage, it is called a step-down transformer.

At each transformer has an input named primary winding and a secondary winding output named. The transformer has an iron core for low frequency and high frequency ferrite core or some that do not have a nucleus (core air).
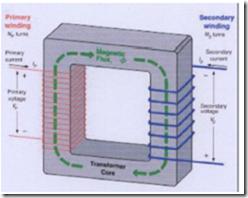
Chart traversed Electric Current Transformer When on the primary winding by an alternating current (AC), the primary winding will be the magnetic field direction magnitnya also commute. This magnetic field will induce secondary winding and the secondary winding flows resulted in an alternating current (AC). Suppose the primary winding current flows berfasa positive (+), then the secondary windings berfasa currents flow negative (-).
Because the primary digulungan currents flowing back and forth, then on a roll sekunderpun flow of alternating current. The amount of power on the primary winding is equal to the power supplied to the secondary winding.
So,
Pp = Ps or Up.Ip = Us.Is
Where:
Pp = primary power in watts
Ps = secondary power in watts
Up = primary voltage in volts
Us = secondary voltage in volts
Ip = primary currents in amperes
Is = secondary currents in amperes
Example: A power transformer is connected with the grid voltage is 220 V, the current flowing in the primary winding of 0.2 amperes. If the secondary voltage of 12 V. Calculate the magnitude of the secondary current.
Completion: Up.Ip = Us.Is 220.0,2 = 12. Is Is Is = 44/12 = 3.66 ampere
Comparison of Transformation:
In general, the number of primary windings is not equal to the number of secondary windings. StepUp to the transformer primary winding amount less than the number of secondary windings, contrary to stepdown transformer primary winding number greater than the number of secondary windings. The number of primary winding and the secondary winding number indicates the magnitude of the primary voltage and secondary voltage magnitude. The greater the voltage the more windings.
Thus the number of windings is proportional to the magnitude of the voltage in the respective sides. If the secondary winding and primary winding = Ns = Np, then the ratio of the number of windings of primary and secondary windings is called comparison transformation and expressed by T = Np / Ns. In the transformer equation applies: Up / Us = Np / Ns or T = Up / Us
Example: A power transformer primary voltage of 220 V, the secondary voltage 30 V. The number of primary windings 1100 convolution.
Calculate the number of secondary windings.
Resolution: Up / Us = Np / Ns 220/30 = 1100 / 7.33 = 1100 Ns / Ns Ns = 1100 / 7.33 Ns = 150.06, gimped
In the electronics technique known various transformers, for both high frequency and low frequency. Example transformers for high-frequency oscillator that transformer, transformer intermediate frequency (IF), transformer spull antenna (tuner). While the transformer is used for low frequency is input transformer, output transformer, transformer filter (choke).