A transistor is a component which is the main building of the development of electronics. Semiconductor devices are typically classified into two major divisions, namely: Juction Bipolar Transistors (BJT) or commonly called the A and Field Effect Transistor Transistor (FET). This chapter, and the next several chapters, will discuss the characteristics, configuration and use of transistors in electronic circuits. In general, the transistors used in three functions: as a switch, the signal shaper and amplifier circuit. An example of a transistor and the terminals are shown in Fig.
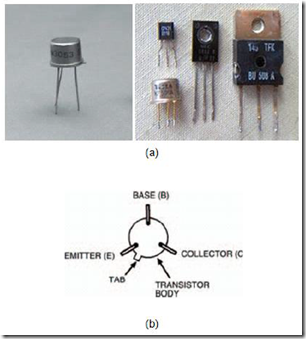
Transistor (a) Physical and (b) Diagram
Transistors are 3 terminal device (foot) and consists of two different types, namely transistor NPN and PNP transistors. Block diagram, schematic and symbol transistors, both NPN and PNP can be seen in Figure 8.2.Transistor created by combining the 3-chip semiconductors by doping and thickness are different. 1 NPN transistor has an area p flanked by two regions n, while the PNP transistor has one area n which is flanked by two regions n.
The merger of the three terminals, then there are two junctions (junction) between regions n and p regions. This linkage has the characteristics as a regular diode, which has been discussed in previous modules.
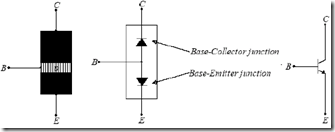
(A) Block diagram, schematic, and symbols
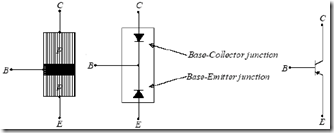
(B) Block diagram, schematic, and the symbol (a) Transistor NPN and (b) PNP Transistor
As shown in the image above, terminals of transistors called the emitter (E), Base (B), and collector (C). Didop emitter terminal is very much the part being, Base didop with very little concentration at the thinnest part, and collectors didop moderately large part. Pendopan and this division would be beneficial to support the functions and ways of working transistors. Figure below shows a cross section of the semiconductor fabricated to make a transistor.
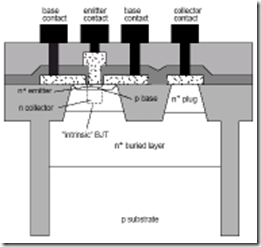
Penampang Transistor
Doping concentration ratio between the terminal base, collector and emitter are 10, 15, 10 17 and 10 19. Thus, the electrical properties of each terminal is not symmetrical, and each output can not be exchanged. To avoid confusion, the initial discussion, only to be focused on the first NPN transistor.