This theory is generally used specifically to analyze the communication network. The overall efficiency of the network hired a maximum power to each branch is 50%. Therefore, the application of this theory for power transmission and distribution network is very limited. Where expected on the transmission and distribution network is a high efficiency rather than the transfer of maximum power.
In cases of a communications network, often a network intended to receive or transmit maximum power efficiency even less. Suppose if power is transferred only in the size of milliwatts or microwatt. The problems are related to the transfer of maximum power workmanship transmission wires and antennae are quite critical. The application on the network direct current (DC), then this theory can be defined as follows:
A resistive load will take a maximum power of a network, if the load is equal to the detention of prisoners from the network, seen from the output terminal, with all of the voltage source is eliminated and only prisoners who live therein.
Examples:
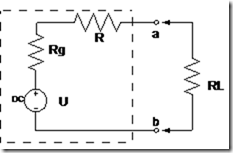
Figure 4.5 Circuit equivalent to the electricity network
Rg = prisoners in generator
R = custody conductor
RL = load resistance
Rg + R = custody network
According to this theory, the RL will take the maximum power of the network if RL = Ri where Ri is the total resistance network in this case Rg + R.
Analysis:
The circuit current is:
![]()
To achieve maximum PL becomes, then:
![]()
Finally found: 2 RL = RL + RL = Ri Ri or (proven)