Transistors are electronic components that are designed as a current amplifier, thereby transistor also called device (device) which handles current (current handling device). See figure 16.
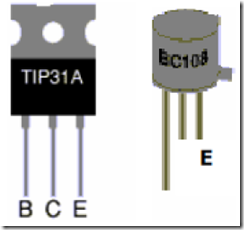
Figure 16. Transistor
Judging from the type, the transistor is divided into two, namely the type PNP (Positive-Negatip- Positive) and type NPN (Negative-Positive-negative). Inlet (leads) to the transistor (commonly known as foot transistor) named with: Base (Base), Collector (Collector), and emitter (Emitter). Transistor is basically two diodes connected in reversed. The first diode is formed by the emitter-base, the second diode is formed by the base-collector.
In the PNP-type transistor, emitter and collector serves as the anode (+) to the base, while the base serves as a cathode (-) of the emitter and the emitter. In type transistor NPN, Base serves as Anode (+) to the emitter and collector, while the emitter and collector serves as the cathode (-) to the Base. Observe carefully drawing 17.
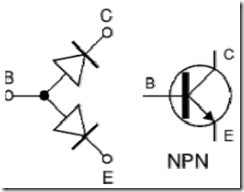
Figure 17. Configuration and Symbols Transistor
The concept of the diodes on the transistor is important to be well understood, because it is closely related to the use Multimeter to measure the value of the unit Ohm of the transistor (read your description of the material on the battery Multimeter). Things to remember when measuring transistor with Multimeter is:
A. On cable PNP-type transistor investigator (probes) red (+) is always placed at the feet Base, investigators cable (probes) black (-) placed alternately on foot emitter and collector.
B. At NPN type transistor investigators cable (probes) black (-) always be placed on foot base, investigators cable (probes) red (+) placed alternately on foot emitter and collector.
C. The switch in the position measuring range Ohms (Ω) and the limit of measurement (range) in the position of x1, x10, or x1kΩ, as needed. See Figure 18.
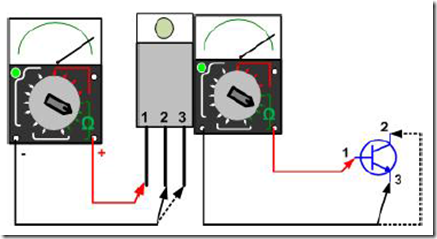
Figure 18. Measurement of Transistor
The legs emitter, base and collector of a transistor can be determined in three ways:
A. By looking at the marks on the body (case) transistor. Some factories transistor made black dots or marks circle on the collector of transistor cylindrical. See figure 19.
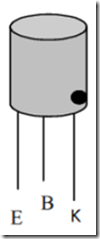
Figure 19. Walking Transistor Cylinder shape
B. By using catalogs dikeluarkanoleh transistor transistor manufacturer.
C. By looking at the small fin protruding from the body of the transistor. Look again at the picture 16.
D. By using Multimeter.
E. For power transistors (power transistors) functioning as a collector transistor body. See figure 20.
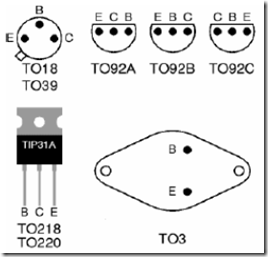
Figure 20. The legs transistors viewed from below