1). Physical-morphological properties
Kimpul bulb type, as well as other tubers are gadung, arrowroot that has been discussed before and the bulbs gembili and suweg which will be discussed later, is a tuber that is rarely encountered around us. According to Irawan (2012), the shape of cymbals (Xanthosoma violaceum Schott) cylinder until somewhat round, there are internode or segment with some buds. The number of child tubers can reach 10 pieces or more, with a length of about 12-25 cm and a diameter of 12-15 cm and the resulting tuber usually weighs 300-1000 grams.
Transverse tuber crossbows show that the tuber structure of the kimpul consists of skin, cortex and phloem vessels and xylem. The bulb skin has a thickness of about 0.01 – 0.1 cm, while the cortex is 0.1 cm thick. In the phloem and xylem vein there are starch grains. Profile of kimpul bulbs can be seen in the following figure.

Figure 2.16. Kimpul ( Xanthosoma violaceum Schoot)
2) Chemical properties
The main components of kimpul bulbs such as other tubers are high enough carbohydrates ranging from 31.0 to 34.2 g per 100 grams of material. High carbohirat content, will produce high energy as well. In addition to carbohydrates, kimpul bulbs also contain fat, protein, vitamins and minerals. The chemical composition of cauliflower depends on varieties, climate, soil fertility and harvest age. The chemical composition of the umi kimpul can be seen in Table 2.15.
Table .15. Chemical composition of koin bulbs per 100 grams of material

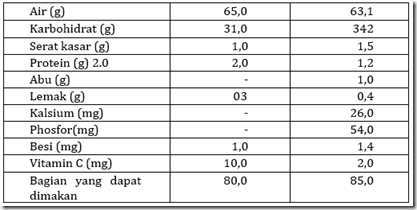
Tuber kimpul often have itching, especially on the parent tubers. The itchiness is caused by the crystals of calcium oxalate formed like a needle. Calcium oxalate can be reduced by washing with plenty of water. In addition, itching can also be removed by steaming and boiling.